| Maria Ilieva - 20 days in
MPI of Microstructure
Physics, Halle, Germany (08.10.2005 - 28.10.2005) Theme: Investigations of metal-polymer composite samples, synthesized in the Laboratory of electroconductive polymers and metal-polymers composites at the Institute of Physical Chemistry (IPC) The following techniques for characterization of the samples were used: High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM), Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy (EELS), High Resolution Electron Microscopy (HREM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDXS) including analysis of light chemical elements. The aim of the joints experiments was to investigate the surface morphology, elemental composition, size of deposited micro- and nano particles and the nature of chemical bonds of two types of metal-polymer composite materials. |
| Teodora Zaprianova - 03.04.2006
- 29.04.2006 - visit to Institute
of Thin Films and Interfaces, Research Center Juelich, Germany Theme: Cooperation research on “Electrochemical deposition of metal nanoclusters and decoration of crystalline and amorphous surfaces”. The aim of the experiments was to study the electrochemical nucleation and growth of metal nano-clusters and to obtain information on the spatial distribution of active sites for nucleus formation on crystalline and amorphous substrates. Au(111), n-Si(111) and glassy carbon were used as working electrodes for electrodeposition of copper crystals by means of single- and double pulse potentiostatic methods. |
| Kamelia Kamburova - one month
(27.03.2006 25.04.2006) in the University
of Bayreuth, Germany. Theme: Scientific investigations of nanoparicles and polyelectrolyte-colloid complexes with electric birefringence. The planned experiments provided additional information about the optical and electrical properties of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (NaCMC) in a solution and after its adsorption on ellipsoidal â-FeOOH particles. This is important for elucidation of the mechanism of formation of multilayer films from biopolymers, being of great interest for creating biocompatible coatings and drug delivery systems. |
|
Bogdan Ranguelov - two months
stay at Centre de Recherche en Matiere
Condensee et Nanosciences, CRMC-N/CNRS, Team Morphologie-Croissance,Luminy,
Marseille, France (02.03.2006 - 02.05.2006):
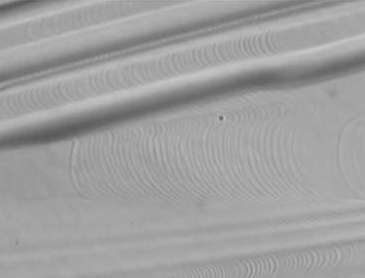
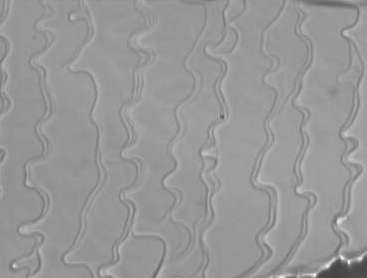
images: Si(111) surface at ~ 1550K. Large group of bunches of steps is clearly visible. |